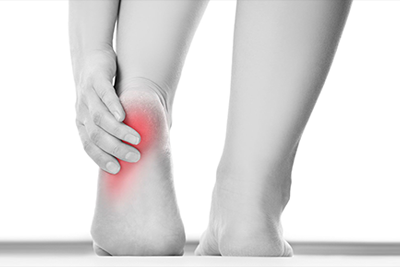
Callus and CornsCallus
Normally, a callus will form on any part of the skin exposed to friction over a long period of time. For example, people often develop calluses on the middle finger of their dominant hand due to writing with a pen or pencil. Although often found on the foot (where the most pressure and friction are applied), calluses can occur anywhere on the body as a reaction to moderate, constant "grinding" pressure. Corn
A corn (or clavus, plural clavi) is a specially shaped callus of dead skin that usually occurs on thin or glabrous (hairless and smooth) skin surfaces, especially on the dorsal surface of toes or fingers. They can sometimes occur on the thicker palmar or plantar skin surfaces. Corns form when the pressure point against the skin traces an elliptical or semi-elliptical path during the rubbing motion, the center of which is at the point of pressure, gradually widening. If there is constant stimulation of the tissue producing the corns, even after the corn is surgically removed, the skin may continue to grow as a corn. The hard part at the center of the corn resembles a funnel with a broad raised top and a pointed bottom. Because of their shape, corns intensify the pressure at the tip and can cause deep tissue damage and ulceration. The scientific name for a corn is heloma (plural helomata). A hard corn is called a heloma durum, while a soft corn is called a heloma molle. The location of the soft corns tends to differ from that of hard corns. Hard corns occur on dry, flat surfaces of skin. Soft corns (frequently found between adjacent toes) stay moist, keeping the surrounding skin soft. The corn's center is not soft however, but indurated. Prevention
Corns and calluses are easier to prevent than to treat. When it is usually not desirable to form a callus, minimizing rubbing and pressure will prevent callus formation. Footwear should be properly fitted, gloves may be worn, and protective pads, rings or skin dressings may be used. People with poor circulation or sensation should check their skin often for signs of rubbing and irritation so they can minimize any damage. |
Additional Services |
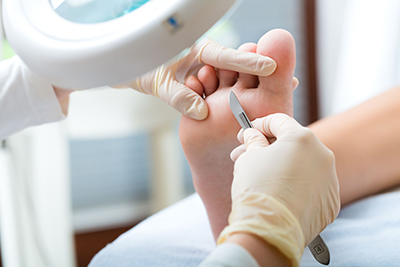
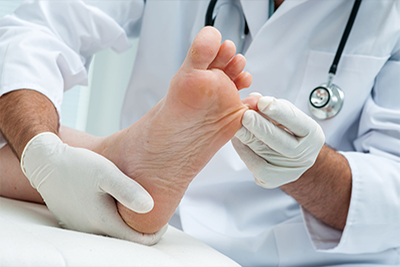
Treatment
Calluses and corns may go away by themselves eventually, once the irritation is consistently avoided. They may also be dissolved with keratolytic agents containing salicylic acid, sanded down with a pumice stone or silicon carbide sandpaper or filed down with a callus shaver, or pared down by a podiatrist.
Calluses and corns may go away by themselves eventually, once the irritation is consistently avoided. They may also be dissolved with keratolytic agents containing salicylic acid, sanded down with a pumice stone or silicon carbide sandpaper or filed down with a callus shaver, or pared down by a podiatrist.