Plantar Fasciitis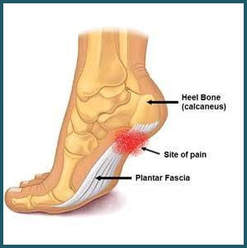
Patient Education Videos
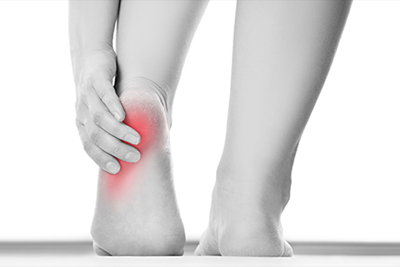
Plantar fasciitis is a disorder that results in pain in the heel and bottom of the foot. The pain is usually most severe with the first steps of the day or following a period of rest. Pain is also frequently brought on by bending the foot and toes up towards the shin and may be worsened by a tight Achilles tendon. The condition typically comes on slowly. In about a third of people both legs are affected. Most cases of plantar fasciitis resolve with time and conservative methods of treatment. Usually for the first few weeks people are advised to rest, change their activities, take pain medications, and stretch. If this is not sufficient physiotherapy, orthotics, splinting, or steroid injections may be options. If other measures do not work extracorporeal shockwave therapy or surgery may be tried. Signs and symptoms
When plantar fasciitis occurs, the pain is typically sharp and usually unilateral (70% of cases). Heel pain is worsened by bearing weight on the heel after long periods of rest. Individuals with plantar fasciitis often report their symptoms are most intense during their first steps after getting out of bed or after prolonged periods of sitting. Improvement of symptoms is usually seen with continued walking. Rare, but reported symptoms include numbness, tingling, swelling, or radiating pain. Typically there are no fevers or night sweats. If the plantar fascia continues to be overused in the setting of plantar fasciitis, the plantar fascia can rupture. Typical signs and symptoms of plantar fascia rupture include a clicking or snapping sound, significant local swelling, and acute pain in the sole of the foot. Treatment
Non-surgical About 90% of plantar fasciitis cases will improve within six months with conservative treatment. Many treatments have been proposed for plantar fasciitis. First-line conservative approaches include rest, heat, ice, and calf-strengthening exercises; techniques to stretch the calf muscles, Achilles tendon, and plantar fascia; weight reduction in the overweight or obese; orthotics; and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as aspirin or ibuprofen. NSAIDs are commonly used to treat plantar fasciitis, but fail to resolve the pain in 20% of people. Surgery Plantar fasciotomy is often considered after conservative treatment has failed to resolve the issue after six months and is viewed as a last resort. Minimally invasive and endoscopic approaches to plantar fasciotomy exist but require a specialist who is familiar with certain equipment. The availability of these surgical techniques is currently limited. Heel spur removal during plantar fasciotomy has not been found to improve the surgical outcome. Plantar heel pain may occur for multiple reasons and release of the lateral plantar nerve branch may be performed alongside the plantar fasciotomy in select cases. Possible complications of plantar fasciotomy include nerve injury, instability of the medial longitudinal arch of the foot, fracture of the calcaneus, prolonged recovery time, infection, rupture of the plantar fascia, and failure to improve the pain. Coblation surgery has recently been proposed as alternative surgical approaches for the treatment of recalcitrant plantar fasciitis. |
Additional Services |
Additional Conditions and Treatments
Book Your Appointment Today |